Can CBD help prevent tooth decay? A study says yes
Author: Lucie Garabasova
A study conducted in 2023, with contributions from leading Czech universities, evaluates the antimicrobial effects of phytocannabinoids (CBD, CBG, CBN, and CBC) on selected oral bacteria. How did the study turn out, and what does it mean for us in practice? We’re happy to share!
Czech study on the effects of phytocannabinoids on oral bacteria
The growing interest in cannabinoids from the cannabis plant prompted the authors of this study to explore and assess the antimicrobial effects of four non-psychotropic phytocannabinoids on selected oral bacteria.
Specifically, the study focused on well-known phytocannabinoids: CBD (found in CBD products), CBG (found in CBG products), CBN, and CBD.
Antimicrobial effects were determined in vitro using a standard microdilution technique
- Porphyromonas gingivalis - This bacterium is primarily responsible for chronic gum disease, gingivitis chronica. If untreated, the inflammation develops into periodontitis
- Streptococcus mutans - Significantly contributes to the formation of tooth decay.
- Lactobacillus acidophilus - A lactic acid-producing bacterium.
- Agregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans - A non-motile bacterium believed to contribute to chronic periodontitis.
- Eikenella corrodens
- L. casei
Study results: Effects of CBD on oral bacteria
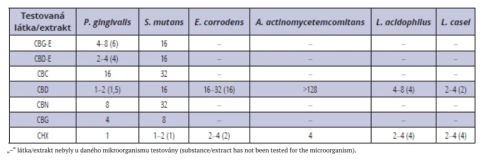
The following table shows that cannabinoids inhibit the growth of bacteria in the oral cavity. All values are compared to chlorhexidine, a substance classified as an antiseptic, i.e., an antimicrobial agent intended for application on living tissue (skin, mucous membranes). It affects a wide range of microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and some fungi. Since its effect on bacteria has been proven, chlorhexidine is also classified as an antibacterial agent.
Table 1. MIC (μg/ml) of tested phytocannabinoids and extracts (CBD-E and CBG-E) compared to chlorhexidine (CHX).
The table shows the range of measured values, with the median shown in parentheses.
The tested complex mixtures did not exhibit significantly higher antimicrobial effects compared to individual phytocannabinoids.
Study conclusion
The study concludes that CBD inhibits the growth of bacteria in the oral cavity, thereby contributing to reduced tooth decay and improved oral hygiene.
Specifically, this study shows that non-psychotropic phytocannabinoids (mainly CBD) inhibit selected bacteria that are part of the oral microbiota. They are also capable of inhibiting the growth of periopathogenic bacteria such as P. gingivalis and, in the case of CBD, also E. corrodens, suggesting the potential for further research and application in dentistry.
How to take preventive care of your oral cavity with CBD?
Apart from the study, here are some tips on how to prevent bacterial overgrowth in the mouth with CBD.
Try using a CBD spray, which, in addition to CBD, also contains colloidal silver, offering further benefits for oral health. We recommend applying the CBD spray about once a day after brushing your teeth as a final step in oral care.